Athens Podiatry Group
Flat Rock Office
Athens Podiatry Group
19723 Allen Rd
Brownstown Twp, MI 48183 USA
Monday:
9:00 am - 5:00 pm
Tuesday:
9:00 am - 5:00 pm
Wednesday:
9:00 am - 5:00 pm
Thursday:
9:00 am - 6:00 pm
Friday:
9:00 am - 3:00 pm
Saturday:
9:00 am - 12:00 pm
every other Saturday
Sunday:
Closed
Flat Rock Office
14835 Telegraph Rd
Flat Rock, MI 48134 USA
Monday:
9:00 am - 5:00 pm
Tuesday:
9:00 pm - 11:30 am
Wednesday:
Closed
Thursday:
9:00 am - 5:00 pm
Friday:
9:00 am - 3:00 pm
Saturday:
Closed
Sunday:
Closed
- Welcome! >
- Articles >
- Bone/Joint/Tendon >
- Chronic Ankle Instability
What Is Chronic Ankle Instability?
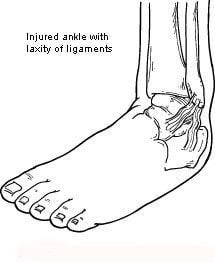
 Chronic ankle instability is a condition characterized by a recurring “giving way” of the outer (lateral) side of the ankle. This condition often develops after repeated ankle sprains. Usually the “giving way” occurs while walking or doing other activities, but it can also happen when you’re just standing. Many athletes, as well as others, suffer from chronic ankle instability.
Chronic ankle instability is a condition characterized by a recurring “giving way” of the outer (lateral) side of the ankle. This condition often develops after repeated ankle sprains. Usually the “giving way” occurs while walking or doing other activities, but it can also happen when you’re just standing. Many athletes, as well as others, suffer from chronic ankle instability.
People with chronic ankle instability often complain of:
- A repeated turning of the ankle, especially on uneven surfaces or when participating in sports
- Persistent (chronic) discomfort and swelling
- Pain or tenderness
- The ankle feeling wobbly or unstable
Causes
Chronic ankle instability usually develops following an ankle sprain that has not adequately healed or was not rehabilitated completely. When you sprain your ankle, the connective tissues (ligaments) are stretched or torn. The ability to balance is often affected. Proper rehabilitation is needed to strengthen the muscles around the ankle and “retrain” the tissues within the ankle that affect balance. Failure to do so may result in repeated ankle sprains.
Repeated ankle sprains often cause – and perpetuate – chronic ankle instability. Each subsequent sprain leads to further weakening (or stretching) of the ligaments, resulting in greater instability and the likelihood of developing additional problems in the ankle.
Diagnosis
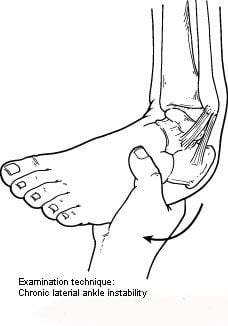
In evaluating and diagnosing your condition, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask you about any previous ankle injuries and instability. Then he or she will examine your ankle to check for tender areas, signs of swelling, and instability of your ankle as shown in the illustration. X-rays or other imaging studies may be helpful in further evaluating the ankle.
 Non-Surgical Treatment
Non-Surgical Treatment
Treatment for chronic ankle instability is based on the results of the examination and tests, as well as on the patient’s level of activity. Non-surgical treatment may include:
- Physical therapy. Physical therapy involves various treatments and exercises to strengthen the ankle, improve balance and range of motion, and retrain your muscles. As you progress through rehabilitation, you may also receive training that relates specifically to your activities or sport.
- Bracing. Some patients wear an ankle brace to gain support for the ankle and keep the ankle from turning. Bracing also helps prevent additional ankle sprains.
- Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
When Is Surgery Needed?
In some cases, the foot and ankle surgeon will recommend surgery based on the degree of instability or lack of response to non-surgical approaches. Surgery usually involves repair or reconstruction of the damaged ligament(s). The surgeon will select the surgical procedure best suited for your case based on the severity of the instability and your activity level. The length of the recovery period will vary, depending on the procedure or procedures performed.
Our Locations
Find us on the map
Hours of Operation
Our Regular Schedule
Athens Podiatry Group
Monday:
9:00 am-5:00 pm
Tuesday:
9:00 am-5:00 pm
Wednesday:
9:00 am-5:00 pm
Thursday:
9:00 am-6:00 pm
Friday:
9:00 am-3:00 pm
Saturday:
9:00 am-12:00 pm
every other Saturday
Sunday:
Closed
Flat Rock Office
Monday:
9:00 am-5:00 pm
Tuesday:
9:00 pm-11:30 am
Wednesday:
Closed
Thursday:
9:00 am-5:00 pm
Friday:
9:00 am-3:00 pm
Saturday:
Closed
Sunday:
Closed
